Binary Search

Les Tours Vertes La Rochelle, 1913, Paul Signac
- 1. What is Binary Search?
- 2. Time complexity of Binary Search
- 3. Binary Search Implementation
- 4. Python Binary Search Library
- 5. What is Parametric Search?
- 6. Binery Search Example Problem
1. What is Binary Search?
Sequential Search : A method of checking data one by one from the front to find specific data in a list
Binary Search : A method of searching for data in a sorted list by halving the search range.
- Binary search sets the search range using the starting point, the ending point, and the midpoint.
[Step 1] Start point: 0, End point: 9, Mid point: 4 (remove decimal point) 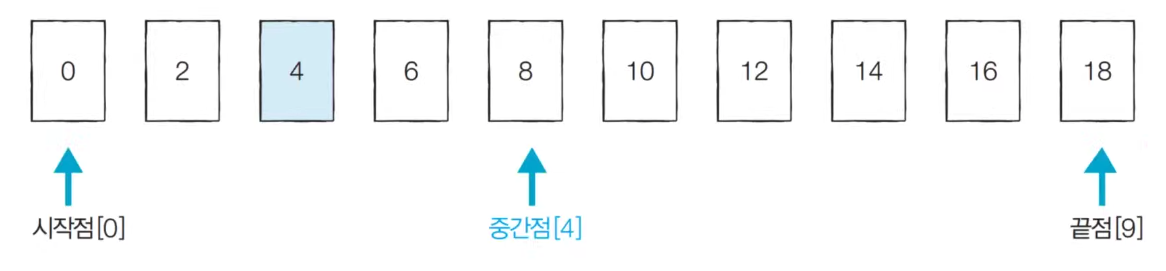
Comparing the midpoint value with the value to be found, if the midpoint value is larger, there is no need to check the midpoint to the right end. Move the end point in front of the midpoint.
[Step 2] Start point: 0, End point: 3, Mid point: 1 (remove decimal point) 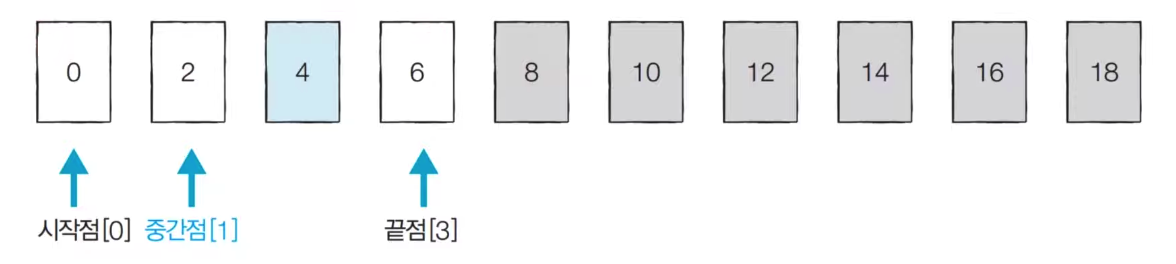
If the midpoint value is smaller than the midpoint value and the value to be found, there is no need to check the midpoint to the left end. Move the starting point behind the midpoint.
[Step 3] Start point:2, End point:3, Mid point: 2 (remove decimal point) 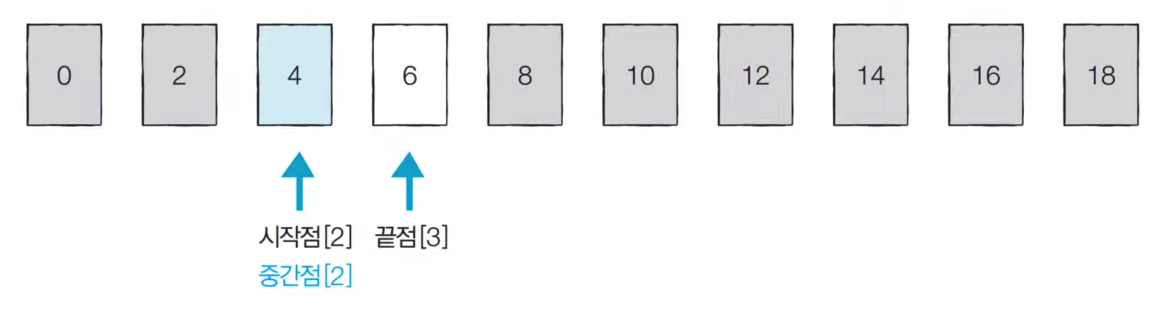
Since we found the value we are looking for at the starting point, we end our search.
2. Time complexity of Binary Search
Since each step is equivalent to dividing the search range by 2, the number of operations is proportional to \(\bf{log_2N}\).
For example, when the initial number of data is 32,
- After step 1, ideally only 16 pieces of data are left.
- After step 2, only about 8 pieces of data remain.
- After step 3, only about 4 pieces of data are left.
In other words, binary search cuts the search range by half, and the time complexity is guaranteed to be \(\underline{O(logN)}\).
3. Binary Search Implementation
Recursive Implementation
# title : 'BinarySearchRecursive.py'
def binary_search(array, target, start, end):
if start > end:
return None
mid = (start + end) // 2
# Convert midpoint index if found
if array[mid] == target:
return mid
# If the value you want to find is less than the value of the midpoint, check the left
elif array[mid] > target:
return binary_search(array, target, start, mid - 1)
# If the value you want to find is greater than the value of the midpoint, check the right
else:
return binary_search(array, target, mid + 1, end)
# Get n (number of elements) and target (value to find)
n, target = list(map(int, input(). split()))
# Get all elements input
array = list(map(int, input(). split()))
# Output the result of binary search
result = binary_search(array, target, 0, n - 1)
if result == None:
print("The element does not exist.")
else:
print(result + 1)
Iterative Implementation
# title : 'BinarySearchIterative.py'
def binary_search(array, target, start, end):
while start <= end:
mid = (start + end) // 2
# return midpoint index if found
if array[mid] == target:
return mid
# If the value you want to find is less than the value of the midpoint, check the left
elif array[mid] > target:
end = mid - 1
# If the value you want to find is greater than the value of the midpoint, check the right
else:
start = mid + 1
return None
# Get n (number of elements) and target (value to find)
n, target = list(map(int, input(). split()))
# Get all elements input
array = list(map(int, input(). split()))
# Output the result of binary search
result = binary_search(array, target, 0, n - 1)
if result == None:
print("The element does not exist.")
else:
print(result + 1)
4. Python Binary Search Library
bisect_left( a, x ): returns the leftmost index at which to insert x into array a while maintaining sorted order
bisect_right( a, x ): returns the rightmost index at which to insert x into array a while maintaining sorted order
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect_right
a = [1, 2, 4, 4, 8]
x = 4
print( bisect_left( a, x ) ) (output) 2
print( bisect_right( a, x ) ) (output) 4
Count the number of data whose values fall within a specific range
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect_right
#Function returning the number of data whose values are [ left_value, right_value ]
def count_by_range( a, left_value, right_value ):
right_index = bisect_right( a, right_value )
left_index = bisect_left( a, left_value )
return right_index - left_index
#declare an array
a = [1, 2, 3, ,3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 8, 9]
#Output the number of data whose value is 4
print( count_by_range(a, 4, 4) ) (output) 2
#Output the number of data whose value is in the range [-1, 3]
print( count_by_range( a, -1, 3) ) (output) 6
5. What is Parametric Search?
Optimization problem is a problem of reducing the value of a function as low as possible or increasing it as much as possible.
Parametric search is a technique for solving an optimization problem into a decision problem (yes or no).
Example: An optimization problem that quickly finds the most appropriate value that satisfies a specific condition
In general, the parametric search problem in coding tests can be solved using binary search.
6. Binery Search Example Problem
6.1 Problem : Making tteokbokki rice cakes
Today, Chan decided to work in a rice cake shop on behalf of her parents who were traveling. Today is the day to make tteokbokki rice cakes. Interestingly, the length of the tteokbokki rice cake is not uniform. Instead, the total length of the rice cakes in one bag is cut with a cutter and adjusted.
If you designate the height (H) on the cutter, it cuts the rice cakes in a row at once. Mochi with a height greater than H will be cut off the part above H, and the lower mochi will not be cut.
For example, if you have rice cakes with heights of 19, 14, 10, and 17 cm side by side and you specify a cutter height of 15 cm, the height of the rice cakes after cutting will be 15, 14, 10, and 15 cm. The lengths of the cut rice cakes are 4, 0, 0, and 2 cm in sequence. The customer takes a length of 6 cm.
Write a program to find the maximum value of the height that can be set in the cutter to obtain at least M rice cakes when the total length requested by the customer is M.
Input conditions
In the first line, the number of loaves N and the requested length M are given. (1 <=N <=1,000,000, 1 <=M <=2,000,000,000 )
In the second row, the individual heights of the rice cakes are given. Since the sum of the heights of rice cakes is always greater than M, the customer can buy as many rice cakes as they need.
The height is a positive integer less than or equal to one billion, or zero.
Output conditions
Prints the maximum value of the height that can be set on the cutter to take home at least M rice cakes.
6.2 Solution : Making tteokbokki rice cakes
Just adjust the height H iteratively by performing a binary search until a suitable height is found. (The higher the H, the smaller the truncated value.)
After checking “Can the condition be satisfied by cutting at this height?”, it can be solved by narrowing the search scope according to whether the condition is satisfied (yes or no).
The height of the cutter is an integer from 0 to 1 billion.
When looking at such a large search scope, the first thing that comes to mind is binary search.
[Step 1] Start point: 0, End point: 19, Mid point: 9 (=H, cutting height) 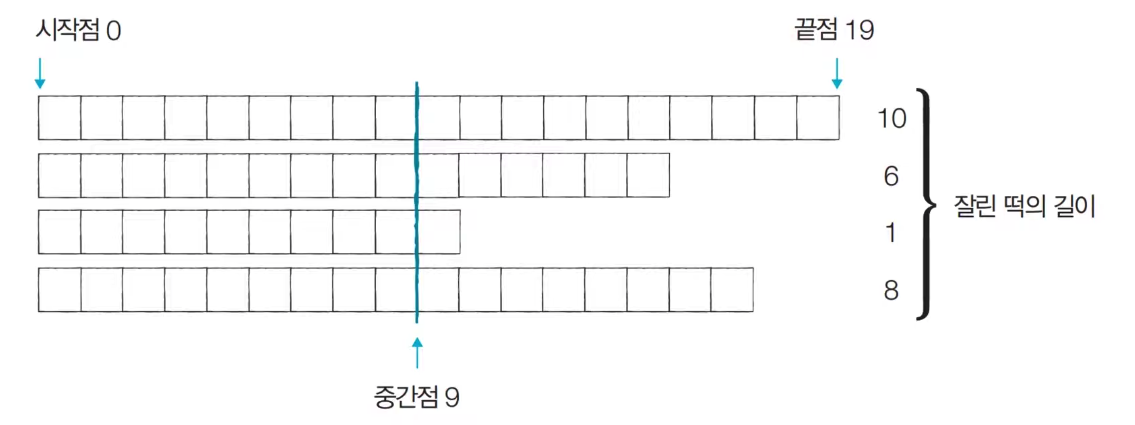
At this time, the required size of the rice cake: M = 6, so the length of the cut rice cake 25 satisfies the minimum. -> Save result
Move the starting point behind the midpoint.
[Step 2] Start Point: 10, End Point: 19, Mid Point: 14 (=H, Cutting Height) 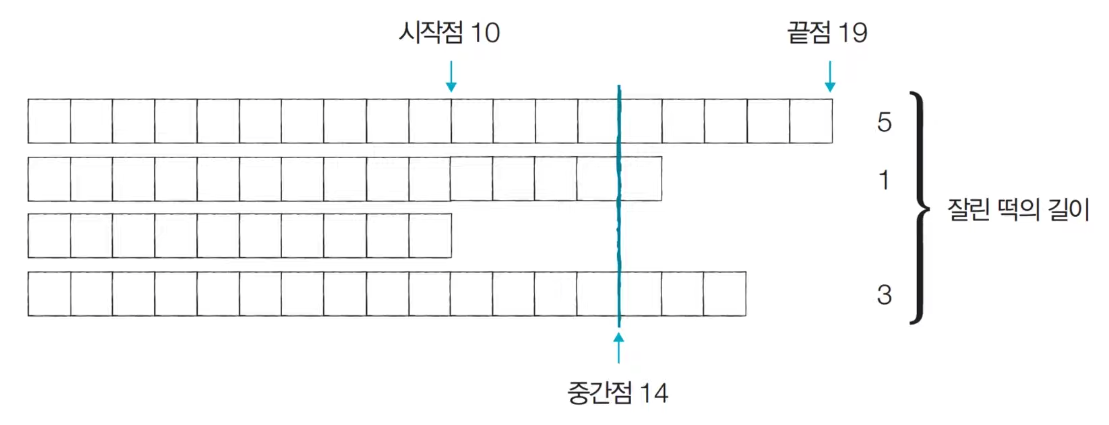
At this time, the required size of the rice cake: M = 6, so the length of the cut rice cake 9 satisfies the minimum. -> Save result
Move the starting point behind the midpoint. (midpoint+1)
[Step 3] Start Point: 15, End Point: 19, Mid Point: 17 (=H, Cutting Height) 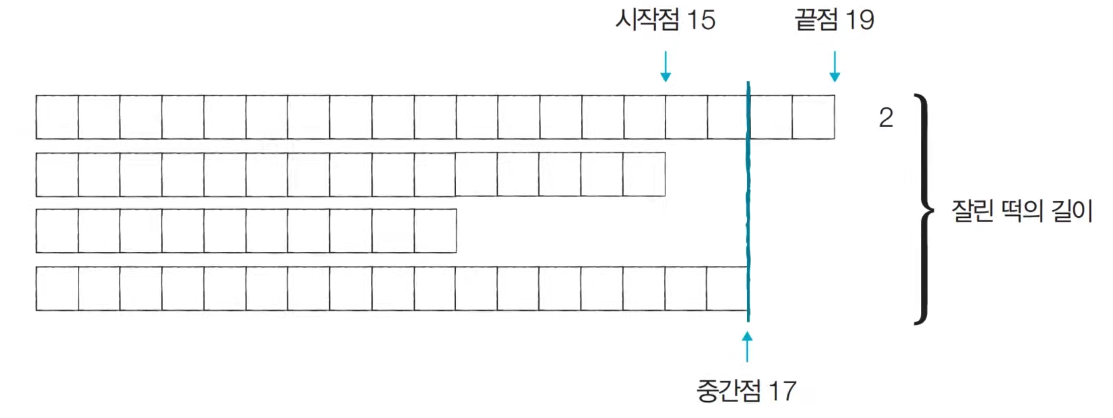
At this time, the required size of rice cake: M = 6, so the length of the cut rice cake 2 does not satisfy the minimum. -> Do not save results
Move the endpoint before the midpoint (midpoint -1).
[Step 4] Start Point: 15, End Point: 16, Mid Point: 15 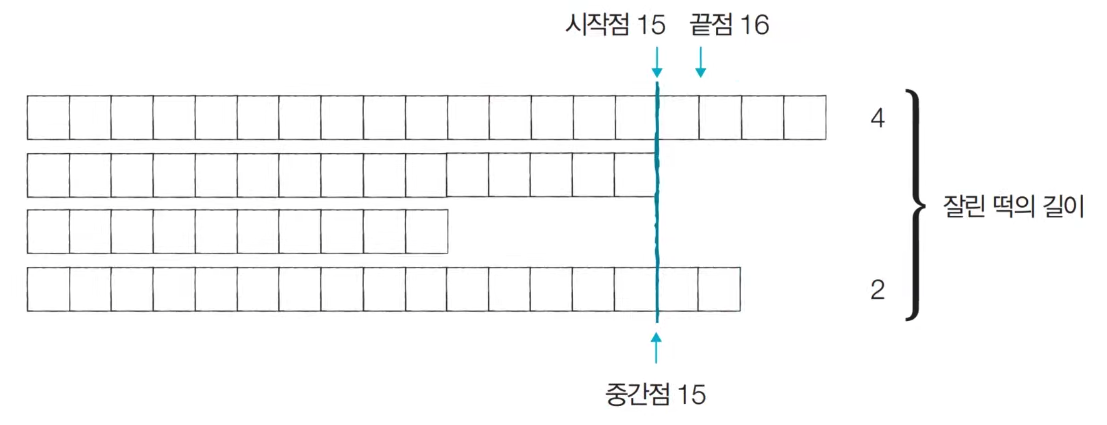
At this time, the required size of rice cake: M = 6, so the length of the cut rice cake 6 satisfies the customer’s desired length. -> Save result
Until we can’t further reduce the search scope using binary search The optimal solution is obtained by changing the starting and ending points, changing H (= midpoint) each time, and checking whether the condition is satisfied when cutting to the current height.
By repeating this binary search process, an answer can be derived.
Since the value of the midpoint becomes an optimized value over time, record the value of the midpoint whenever the sum of the lengths of rice cakes obtained by repeating the process is greater than or equal to the required length of rice cakes (=M). .
# title : 'MakingTteokbokkiRiceCakes.py'
#Enter the number of rice cakes (N) and the requested length of rice cakes (M)
n, m = list( map( int, input() . split( ' ' ))))
#Enter the individual height information of each rice cake
array = list( map( int, input() . split( ' ' ))))
#Set start and end points for binary search
start = 0
end = max( array ) #length of longest rice cake
#Perform binary search (repeat)
result = 0
while( start <=end ):
total = 0
mid = (start + end) // 2
for x in array:
#Calculation of the amount of rice cakes when cut
if x > mid: #When the length (x) of the current rice cake is greater than the height
total += x - mid # Put the cut rice cake into the total variable.
#If the amount of rice cake is insufficient, cut more (Explore the left part)
if total < m:
end = mid -1 #end point forward midpoint
#If the amount of rice cake is sufficient, cut less (search for the right part)
else:
result = mid #The answer is when it is cut as small as possible, so record it in the result here
start = mid + 1 #Move the start point behind the midpoint
#print the correct answer
print( result )
6.3 Problem : Count a specific number in a sorted array
A sequence containing N elements is sorted in ascending order. Count the number of times x appears in this sequence. For example, if there is a sequence {1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3} and x=2, 4 is output because there are 4 elements with a value of 2 in the current sequence.
However, if the algorithm is not designed with a time complexity of \(O(logN)\), this problem is judged to be time-out.
Input conditions
In the first line, N and x are entered in the form of integers separated by spaces.
(1 <= N<=1,000,000), (-109 <= x <=109 )
In the second line, N elements are entered in the form of integers separated by spaces.
Output conditions
Outputs the number of elements whose value is x among the elements of a sequence. However, if there is no element with the value x, -1 is output.
6.4 Solution : Count a specific number in a sorted array
An algorithm that operates with a time complexity of \(O(logN)\) is required.
- In general linear search, it is judged as timeout.
- But since the data is sorted, we can do a binary search.
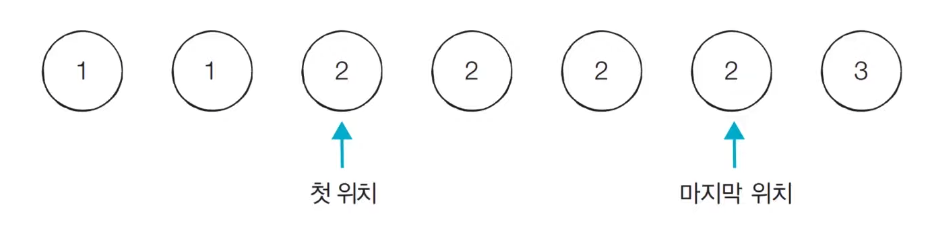
You can solve the problem by finding the first and last positions where a specific value (x) appears and calculating the position difference. Binary search is performed twice over the entire search range. Makes you find the first location, the last location.
# title : 'CountaSpecificNumberInaSortedArray.py'
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect_right
#Function that returns the number of data whose values are [left_value, right_value]
def count_by_range( array, left_value, right_value ):
right_index = bisect_right( array, right_value )
left_index = bisect_left( array, left_value )
return right_index - left_index #left_value or more and right_value or less
n, x = map( int, input() .split( )) # Get the number of data N, the value x to find
array = list( map( int, input() .split( ))) #Get all data input
#Count the number of data whose values are in the range [x, x] = Just count the number of x
count = count_by_range( array, x, x )
#if the element with value x does not exist
if count == 0:
print(-1)
#if there is an element with value x
else:
print( count )
https://www.freecodecamp.org/
https://www.programiz.com/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/
https://blog.naver.com/PostList.naver?blogId=ndb796
이것이 코딩테스트다,2020,나동빈,한빛미디어